Garlic and Stomach Cancer
The normal physiology of cells:
Somatic cells make up about 99 percent of the human body and are constantly changing cells, they grow, divide and also die. Cells are the structural units that make up all living organisms, body functions, nervous system and human anatomy. Cells will have specific functions in the human body. The environment cells are in dilates their function and capacity to effectively keep the human body functioning. During human life time, virtually all the somatic cells in a human body except for brain and nerve cells will be replaced thousands of times. As long as human cells are being produced and replicated in a healthy environment human life function will remain optimal, the body will replace, grow, develop, rebuild and recover though a process called gene expression and cell division. Gene expression has two factors transcription and translation.
Transcription, process by which individual genetic heritage called genes which are hereditary units that control cellular activities are made up of 46 chromosomes, 23 inherited from both paternal and maternal DNA. DNA alone cannot leave the nucleus. Transcription process ensures a copy of DNA is transcribed to a protein strand of RNA.
DNA is a sequence of the specific nucleotide sequence of the gene that is encoded to a protein strand of RNA this is called messenger RNA. (mRNA).
There are 3 sub-phases to this process:
- Initiation
- Elongation
- Termination
Messenger RNA, with the encoded genetic information on the protein exits the nucleolus through nuclear pores through an active transport process and translation process begins;
Also divided into 3 sub phases of:
- Initiation
- Elongation
- Termination
The process of translation will occur outside the nucleus. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is now a template for protein ribosome to bound to the mRNA which are protein molecules stored inside the cell to develop the DNA this process involves reading the unique codon on the mRNA to determine the amino acid sequence of the protein.
The specific amino acid profiling will occur until a corresponding STOP codon will release the peptide chain from the ribosome. A new complete protein has been developed from specific DNA.
Cell Division is a process called mitosis, cells will duplicate to promote growth, healing and generate human new tissue. Mitosis or cell division is the duplicating of already existing cells in your body. Cell division is initiated by a duplication of its own genetic material.
This is done in interphase of the cell which has 3 sub phases:
- G1 phase – the cell metabolic rate increases
- S phase – DNA replication
- G2 -Phase conclusion of the metabolic rate
The end result is the cell doubling the DNA codons to make a genetic counterpart cell.
This is when the cell is actually ready for division (Mitosis).
Mitosis
Mitosis has 4 main stages of cell division:
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
When this structured process of phases is complete cytokinesis will occur, cytokinesis is the complete splitting of a cell to make an identical counterpart for continuous development of new cells which make tissues, tissues will make organs to create systems to perfume organismal functions of the human body.
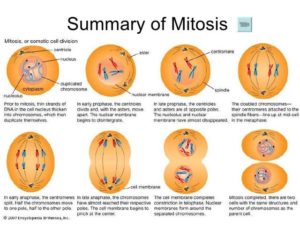
Basic human life function and cell replication
With so many cell divisions occurring throughout the human body, it would be understandable that in some case there would and could be some form of genetic mutation in the DNA that effects the cells capability of performing positive regeneration of the body and start to create an unhealthy replication of cell mitosis. Especially in places where cell division is already occurring rapidly like the gastric region. This can be researched back to mutated proteins and the suppression or inactivity of a protective gene P53. This is where most cancers will stem from, a genetic mutation in the DNA code. These cells could be identified as tumour cells within the human body. Tumour cells or genetically mutated somatic cells can proliferate into cancerous tumours by the same process of healthy cell division. The genetically mutated gene cell should be detected by the P53 tumour suppressor gene in the human bodies defensive mechanism against mutations of healthy cells. Genetic mutations of healthy DNA in cells can be detected by the P53 tumour suppressor gene. (Jurasunas,2015) The P53 tumour suppressor gene is directly involved with the initiation of apoptosis and programmed cell death to prevent the accumulation of abnormal cell growth in the human body. P53 Gene is a protective protocol gene for the human body. Active P53 binds to the target DNA and determines the choice between triggering cell cycle arrests at a check point to allow DNA repair or activation of a pathway leading to the cell death apoptosis. With the loss or decreased activity of the p53 tumour suppressor gene is correlated with 45% of stomach cancers. (Fulda S. 2009). Programmed apoptosis or the activity of P53 tumour suppressor gene is diminished through a number of cellular activities in the human body. The induced exposure to stress response in the human body may contribute to the inactivity of the P53 tumour suppressor gene. This can be contributed to viral or bacterial infections of the stomach. (H. Pylori). Important functions of the nucleoli are connected in and with viral infections, viral proteins are harboured in the nucleoli. Being that the nucleolus produces ribosomes which are sometimes impaired, the stress response from infection may be a contributor to faulty DNA replication. (Stepinski, 2016).
This integral function of the human body is essential in providing genetic stability. Human cytochrome P53 enzyme has proposed to play a role in cellular defence against chemical induced oxidative stress and viral stress. The detection of genetically mutated cells can be P53 tumour suppression gene dependant.
P53 is a novel transcriptional regulator of gene expression and healthy cell replication.
Human cytochrome P450 enzyme has proposed to play a role in cellular defence against chemical induced oxidative stress, P53 is a novel transcriptional regulator of the gene
A meta-analysis showed that high or low intake of garlic were all associated with the reduction risk of gastric cancer. High intake had the most significant risk reduction. The total intake of high levels was reported of >1.5kg/year, >1 time/week, seldom to 1 time/day every day. (Eslick & Kodali, 2015). H. Pylori has been shown to have an increased risk in the development in gastric cancer. Garlic extract has been found to have an antibacterial effect and inhibit the bacterial growth of the H. Pylori. The anticancer mechanisms of allium vegetables come from the hypothesis that the inhibition of carcinogen- induced DNA and the suppression of carcinogen activating enzymes cytochrome P450 that garlic brings. Furthermore, to the suppression of H. Pylori infection which garlic has been shown to have an antibacterial effect on the gastric stress infection. H. Pylori is a key risk factor for gastric cancer. (Guercio, Galeone, Turati & Vecchia, 2014)
Summary
So in short the daily intake of garlic to no less than 1.5kg per year was shown to the decreased H.pylori bacteria in the stomach due to its high anti bacterial effects. H.Pylori has a high risk factor of developing stomach cancer.
Tyrone Jensen Nutritional and Dietetic Medicine Student
Owner/ Operator Tight Fitness Solutions/Head Coach and Trainer
Find out more about Tyrone Click Here
References:
Guercio V, Galeone C, Turati F and Vecchia C L: Gastric Cancer and Allium Vegetable Intake: A Critical Review of the Experimental and Epidermiologic evidence”. 772-773, 2014.
Jurasunas S, The P53 Tumor Suppressor: “Understanding P53 – Based Anti Cancer Therapies Utilizing Dietary Agents”. 2015, Page 67.
Jurasunas S, The P53 Tumor Suppressor: “Understanding P53 – Based Anti Cancer Therapies Utilizing Dietary Agents”. 2015, Page 67. Taken from Fulda S. Tumor resistance to apoptosis. 2009.
Kodali R.T & Eslick G.D, Meta-Analysis: “Does Garlic Intake Reduce Risk Of Gastric Cancer”? 2015 Viewed 20 March 2018
Stepinski D, “Nucleolus‐Derived Mediators in Oncogenic Stress Response and Activation of p53‐dependent Pathways” 2016, Page 121-129


